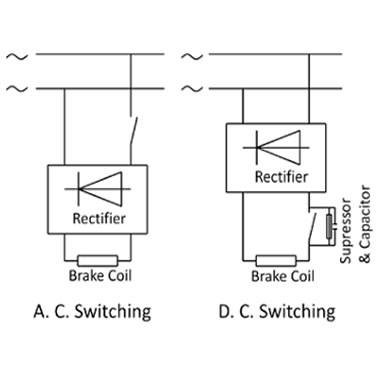
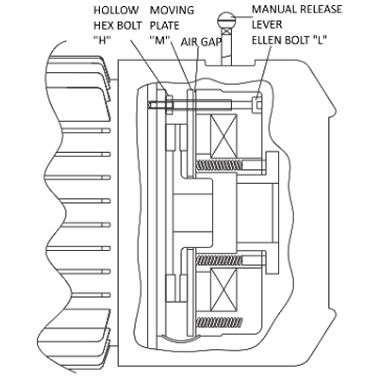
Brake Motor
Brake motors are required when you want the motor to stop quickly even with heavy inertia/load like hoisting, positioning or material movement. "mototek" brake motors are becoming popular due to its practically maintenance free and noise less performance. "mototek" Brake motors are normally supplied with D.C. fail safe brakes, also known as normally ON brake. The motor is braked (Locked) when power is not applied i.e. de-energized to brake. This ensures real fail safe braking. The construction is quite robust and requires very limited maintenance. With wearing of liners on the rotor of brake, the air-gap can be easily adjusted. lf necessary, the rotor can be easily replaced completely as well. The brake is mounted on end covers on non-driving end of the motor. lt comes with a Manual release lever.
Selection Criteria
It is recommended to use proper size of brake. It should not be undersized or should not be over sized as well. Depending uponthe application, the service factor of the brake has to be selected for proper braking.
Service factors for selection for the brake are mentioned in the selection table. This is just a guideline as there are many other factors to be considered while selecting the brake size like mounting positions, type of transmission and type and ratio of reductions. We request you to consult "mototek" for proper selection of brake size.
| OUTPUT | 2-POLE 3000RPM | 4-POLE 1500RPM | 6-POLE 1000RPM | 8-POLE 750RPM | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KW | HP | FRAME | Brake | Safety | FRAME | Brake | Safety | FRAME | Brake | Safety | FRAME | Brake | Safety |
| Size | Torque | Factor | Size | Torque | Factor | Size | Torque | Factor | Size | Torque | Factor | ||
| in Nm | in Nm | in Nm | in Nm | ||||||||||
| 0.18 | 0.25 | 63 | 4.5 | 7.38 | 63 | 4.5 | 3.66 | 71 | 4.5 | 2.43 | 80 | 10 | 4.02 |
| 0.25 | 0.33 | 71 | 4.5 | 5.29 | 71 | 4.5 | 2.63 | 71 | 4.5 | 1.75 | - | - | - |
| 0.37 | 0.25 | 71 | 4.5 | 3.75 | 71 | 4.5 | 1.79 | 80 | 10 | 2.63 | 90S | 10 | 1.95 |
| 0.55 | 0.75 | 71 | 4.5 | 2.39 | 71 | 4.5 | 1.20 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| - | 80 | 10 | 5.32 | 80 | 10 | 2.67 | 80 | 10 | 1.77 | 90L | 20 | 2.63 | |
| 0.75 | 1.00 | 80 | 10 | 3.91 | 80 | 10 | 1.95 | 90S | 20 | 2.60 | 100L | 20 | 1.93 |
| 1.10 | 1.50 | 80 | 10 | 2.67 | 90S | 20 | 2.67 | 90L | 20 | 1.77 | 100L | 40 | 2.63 |
| 1.50 | 2.00 | 90S | 20 | 3.91 | 90L | 20 | 1.96 | 100L | 40 | 2.60 | 112M | 40 | 1.93 |
| 2.20 | 3.00 | 90L | 20 | 2.67 | 100L | 40 | 2.66 | 112M | 55 | 2.43 | 1325 | 60 | 1.97 |
| 3.00 | 4.00 | 100L | 20 | 1.96 | 100L | 40 | 1.96 | 132S | 60 | 1.95 | 132M | 85 | 2.05 |
| 3.70 | 5.00 | 100L | 20 | 1.58 | 112M | 60 | 2.38 | 1325 | 85 | 2.24 | 132M | 150 | 2.93 |
| 5.50 | 7.50 | 112M | 40 | 2.13 | 132S | 85 | 2.27 | 132M | 140 | 2.48 | 160M | 150 | 1.97 |
| 7.50 | 10.00 | 132S | 60 | 2.35 | 132M | 140 | 2.74 | 160M | 150 | 1.95 | 160L | 250 | 2.41 |
| 9.30 | 12.50 | 132M | 60 | 1.89 | 132M | 150 | 2.36 | 160L | 250 | 2.62 | - | - | - |
| 160M | 85 | 2.68 | 160M | 150 | 2.36 | - | - | - | 180M | 250 | 1.94 | ||
| 11.00 | 15.00 | 160M | 85 | 2.27 | 160M | 150 | 2.00 | 160L | 250 | 2.21 | 180L | 250 | 1.64 |
| 15.00 | 20.00 | 160M | 140 | 2.74 | 160L | 250 | 2.44 | 180L | 250 | 1.62 | - | - | - |
| 18.50 | 25.00 | 160L | 150 | 2.38 | 180M | 250 | 1.98 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 22.00 | 30.00 | 180M | 150 | 2.00 | 180L | 250 | 1.67 | - | - | - | - | - | - |